GC Analysis and Testing
GC Analysis and Testing
ACTA Laboratories, Inc. is a cGMP FDA Registered Testing Laboratory that performs GC analyses on Pharmaceutical APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) and Drug Products. ACTA can follow USP, BP, JP, and EP methods or develop methods of analysis for your API or Drug Product. ACTA can perform Method Validation and Verification to meet strict FDA regulatory requirements.
ACTA has the following injection capabilities:
- Liquid Injector (for direct injection of liquids)
- Headspace Injector (Sample sealed in a vial and heated, headspace gas in the vial is injected)
- Gas Sampling Valve (for testing of gas samples in a cylinder or sampling bag)
ACTA has the following detection capabilities:
- FID (Flame Ionization Detector)
- TCD (Thermal Conductivity Detector)
What is GC?
GC (Gas Chromatography) is a separation technique based on a solid Stationary Phase and a gas Mobile Phase. There are 2 types of GC columns, Packed Column and Capillary Column. A Packed column has the Stationary Phase in the form of particles packed into a column (hollow tube containing particles). A Capillary Column has a long capillary (narrow bore tube) with the Stationary Phase is coated onto the inner surface of the capillary. The Mobile Phase is also referred to as the carrier gas (typically nitrogen or helium). Adjusting the temperature of the column (contained in an oven) adjusts how quickly the compounds pass through the column. The sample is injected into the GC injector (heated tube) and the volatile compounds are volatilized into gaseous compounds. The volatilized sample is then flushed into the column using the carrier gas. Different compounds have different affinities to be attracted to (stick to) the particles in the GC column and different affinities to being flushed through the column using the mobile phase. The competition between a compound’s affinity to stick to the stationary phase or get flushed away in the liquid mobile phase is what enables the separation. A mixture of different compounds can be separated by chromatography and then detected individually by a detector (e.g. FID). The detector response for the separated compound will be proportional to the concentration of the compound in solution. Comparison of the detector response for an unknown to that of a known standard (known concentration of a pure compound) can determine the concentration present in the unknown.
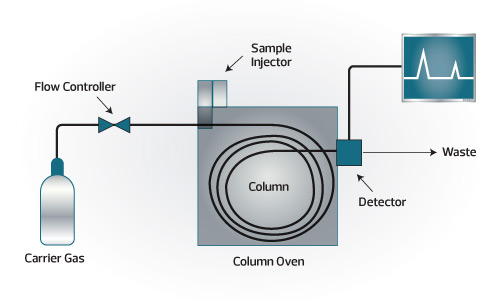
Components of a GC System (in order):
- Carrier Gas with Flow Controller Gas delivery system that flushes Carrier Gas through the GC system
- Injector injects a small quantity of a sample or standard solution (or gas) into the column
- Column a hollow tube filled with porous packing material or coated with stationary phase
- Detector instrument that monitors the gas exiting the GC column and will respond to the compounds of interest in the analysis
- Computer System with Chromatography Software turns detector response into numerical result to determine concentration of each analyte
If you would like to discuss any GC analysis needs, please contact ACTA Laboratories, Inc. at 949-595-0641 or info@actalabs.com
Diagram of a Gas Chromatograph
Please submit a completed form with your samples or send by email to info@actalabs.com
Download Here (48 kb)
Please include a completed form when submitting samples or send by email to info@actalabs.com
Download Here (953 kb)
